Adjustable Mortgage Loan Rates Trends 2024: Shocking Insights
Navigating the world of adjustable mortgage loan rates trends can feel like predicting the weather in a storm. With shifting economic winds, understanding these fluctuations is crucial for smart homeowners and investors alike.
Understanding Adjustable Mortgage Loan Rates Trends

Adjustable mortgage loan rates trends are not just numbers on a screen—they reflect the pulse of the economy, monetary policy, and housing market dynamics. Unlike fixed-rate mortgages, adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) come with interest rates that change over time, typically after an initial fixed period. This makes tracking their trends essential for borrowers aiming to save money or avoid future payment shocks.
What Are Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMs)?
An adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) is a home loan with an interest rate that adjusts periodically based on a benchmark or index. Most ARMs start with a low introductory rate—often lower than fixed-rate mortgages—for a set period, such as 3, 5, 7, or 10 years. After this initial phase, the rate resets according to market conditions, which can lead to higher or lower monthly payments.
Common types include 5/1 ARM, 7/1 ARM, and 10/1 ARM, where the first number indicates the fixed-rate period in years and the second shows how often the rate adjusts afterward.ARMs are tied to financial indexes like the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR), which replaced LIBOR as the primary benchmark in recent years.Lenders add a margin to the index rate to determine your actual interest rate, which remains constant throughout the loan term.How Do Adjustable Mortgage Loan Rates Trends Work?The movement of adjustable mortgage loan rates trends depends on several macroeconomic factors, including inflation, Federal Reserve policy, bond yields, and overall credit market conditions..
When the economy heats up, central banks may raise interest rates to cool inflation, which directly impacts ARM rates after their reset periods..
Rate adjustments are governed by periodic and lifetime caps, limiting how much your rate can increase at each adjustment and over the life of the loan.For example, a 5/1 ARM might have a 2% periodic cap and a 5% lifetime cap, meaning your rate can’t rise more than 2 percentage points per year or 5 points above the initial rate.Understanding these caps is vital for financial planning, especially if you plan to stay in your home long-term.”ARMs can be powerful tools for borrowers who understand the risks and plan accordingly.They offer lower initial payments but come with uncertainty down the road.” — Federal Reserve Consumer GuideHistorical Trends in Adjustable Mortgage Loan RatesTo truly grasp where adjustable mortgage loan rates trends are headed, it’s essential to look back at their historical performance.
.Over the past few decades, ARMs have cycled in and out of favor depending on the broader economic climate and consumer confidence..
The Rise and Fall of ARMs in the 2000s
During the early 2000s, especially between 2003 and 2006, ARMs gained immense popularity due to low initial rates and relaxed lending standards. Many borrowers were lured by the promise of affordability, only to face steep payment increases when rates reset during the housing bubble burst.
- Subprime lending practices amplified the risks, leading to widespread defaults when adjustable mortgage loan rates trends spiked post-2006.
- The collapse of the housing market in 2008 was partly fueled by poorly structured ARMs and a lack of borrower awareness about future rate adjustments.
- This period serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of short-term thinking in mortgage financing.
Post-Crisis Regulation and ARM Resurgence
After the 2008 financial crisis, regulatory reforms like the Dodd-Frank Act introduced stricter underwriting standards and clearer disclosures for ARMs. These changes aimed to protect consumers from predatory lending and ensure they understood the long-term implications of rate adjustments.
- The Qualified Mortgage (QM) rule now requires lenders to verify a borrower’s ability to repay the loan even after the rate adjusts.
- As a result, ARMs became safer and more transparent, paving the way for a cautious comeback in the 2010s.
- By 2021–2022, as fixed mortgage rates began to climb, ARMs regained appeal among savvy borrowers looking to minimize early payments.
Current Adjustable Mortgage Loan Rates Trends in 2024
In 2024, adjustable mortgage loan rates trends are shaped by a complex mix of inflation control efforts, Federal Reserve policy shifts, and global economic uncertainty. While fixed mortgage rates remain relatively high compared to the historic lows of 2020–2021, ARMs are once again attracting attention for their initial cost savings.
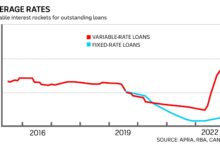
ARM Rates vs. Fixed Rates: A Comparative Look
As of mid-2024, the average 30-year fixed mortgage rate hovers around 6.8%, while a 5/1 ARM averages approximately 6.1%. Although the difference may seem small, it can translate into significant savings over the first five years.
- Borrowers opting for a $400,000 mortgage could save over $100 per month in the initial period with an ARM versus a fixed-rate loan.
- However, these savings come with the risk of higher payments later if interest rates remain elevated or rise further.
- Market analysts suggest that ARMs are most beneficial for those planning to sell or refinance before the first rate adjustment.
Key Drivers Behind Today’s Adjustable Mortgage Loan Rates Trends
Several forces are currently influencing adjustable mortgage loan rates trends:
- Federal Reserve Policy: The Fed’s benchmark federal funds rate directly affects short-term interest rates, which in turn influence ARM indexes like SOFR. Although the Fed paused rate hikes in early 2024, inflation remains above target, keeping upward pressure on rates.
- Inflation and Economic Growth: Persistent inflation, driven by supply chain adjustments and labor market tightness, has delayed expectations of rate cuts. This prolongs higher ARM rates during reset periods.
- Housing Market Demand: With home prices still high in many regions, affordability concerns are pushing some buyers toward ARMs to reduce initial costs.
For real-time data on current ARM rates, visit the Freddie Mac Primary Mortgage Market Survey, which tracks weekly mortgage rate trends across the U.S.
Factors Influencing Future Adjustable Mortgage Loan Rates Trends
Predicting the future of adjustable mortgage loan rates trends requires analyzing both economic indicators and policy decisions. While no one can forecast with absolute certainty, several key variables provide insight into potential trajectories.
Role of the Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve plays a central role in shaping adjustable mortgage loan rates trends through its control of monetary policy. By adjusting the federal funds rate, the Fed influences short-term interest rates, which are closely linked to ARM indexes.
- If inflation continues to moderate, the Fed may begin cutting rates in late 2024 or early 2025, potentially lowering ARM rates for new borrowers.
- Conversely, if inflation rebounds, the Fed could resume rate hikes, leading to higher ARM resets.
- Market expectations, as reflected in futures contracts, suggest a 60% chance of at least one rate cut by Q4 2024 (source: CME Group FedWatch Tool).
Impact of Inflation and Economic Indicators
Inflation remains the biggest wildcard in the outlook for adjustable mortgage loan rates trends. Core inflation (excluding food and energy) has shown signs of cooling but remains above the Fed’s 2% target.
- Strong employment data and wage growth could keep inflation elevated, delaying rate cuts.
- Conversely, a slowdown in GDP growth or rising unemployment could prompt earlier easing, benefiting ARM borrowers.
- Economic indicators like the Consumer Price Index (CPI), Producer Price Index (PPI), and Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) are closely watched by lenders and investors alike.
Global Financial Markets and Investor Sentiment
U.S. mortgage rates, including ARMs, are also influenced by global capital flows. When investors seek safe-haven assets, they often buy U.S. Treasury bonds, which can push yields—and mortgage rates—lower.
- Geopolitical tensions, such as conflicts in Eastern Europe or the Middle East, can increase demand for Treasuries, indirectly affecting ARM rates.
- Similarly, economic instability in major economies like China or the Eurozone can shift investment patterns and impact U.S. interest rates.
- International bond yields and currency exchange rates are therefore indirect but important factors in adjustable mortgage loan rates trends.
Pros and Cons of Choosing an ARM Based on Current Trends
With adjustable mortgage loan rates trends favoring ARMs in the short term, many borrowers are reconsidering this option. However, the decision should be based on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and housing plans.
Advantages of ARMs in Today’s Market
There are several compelling reasons why ARMs are regaining popularity in 2024:
- Lower Initial Payments: The introductory rate on an ARM is typically lower than a fixed-rate mortgage, improving cash flow in the early years.
- Short-Term Homeownership Strategy: If you plan to sell or refinance within 5–7 years, you may never face a rate adjustment.
- Potential for Rate Decreases: If the Fed cuts rates in the coming years, your ARM could reset lower, reducing your payment.
- Flexibility: ARMs offer more options for borrowers who don’t fit the traditional 30-year fixed mold.
Risks and Drawbacks of ARMs
Despite their appeal, ARMs carry inherent risks that must be carefully weighed:
Payment Uncertainty: Your monthly payment can increase significantly after the reset, especially if rates rise.Refinancing Risk: If you plan to refinance before the rate adjusts, you’re dependent on favorable market conditions and your creditworthiness at that time.Long-Term Cost: Over the life of the loan, an ARM could end up costing more than a fixed-rate mortgage if rates trend upward.Complexity: ARMs have more moving parts—indexes, margins, caps, adjustment periods—making them harder to understand than fixed loans.”The key to using an ARM successfully is having an exit strategy.Whether it’s selling, refinancing, or preparing for higher payments, planning is everything.” — National Association of Realtors (NAR)How to Monitor Adjustable Mortgage Loan Rates Trends EffectivelyStaying informed about adjustable mortgage loan rates trends is critical for both current ARM holders and prospective borrowers.
.With rates changing weekly—or even daily—relying on outdated information can lead to poor financial decisions..
Reliable Sources for Tracking ARM Rates
Several authoritative sources provide up-to-date data on mortgage rates, including ARMs:
- Bankrate: Offers weekly updates on 5/1 ARM rates across lenders, along with expert analysis.
- Mortgage News Daily: Provides real-time rate tracking and trend forecasts based on bond market movements.
- FHFA House Price Index: Helps contextualize rate trends with housing market performance.
Using Rate Alerts and Comparison Tools
Technology makes it easier than ever to stay on top of adjustable mortgage loan rates trends:
- Set up rate alerts through lenders or financial websites to receive email or app notifications when ARM rates drop.
- Use mortgage comparison tools like Zillow’s Mortgage Calculator to model different scenarios and see how rate changes affect your payment.
- Consult with a mortgage broker who can monitor trends and advise on optimal timing for locking in a rate.
Strategies for Managing Risk in Adjustable Mortgage Loan Rates Trends
Given the inherent volatility of adjustable mortgage loan rates trends, borrowers must adopt proactive strategies to mitigate financial risk. Whether you already have an ARM or are considering one, smart planning can protect your budget and long-term goals.
Budgeting for Potential Rate Increases
One of the most effective ways to manage ARM risk is to prepare financially for the worst-case scenario:
- Calculate your maximum possible payment using the lifetime cap and ensure your budget can handle it.
- Build an emergency fund to cover higher payments if rates rise unexpectedly.
- Consider making extra principal payments during the fixed period to reduce future interest costs.
Refinancing and Exit Strategies
Having a clear exit plan is crucial when dealing with adjustable mortgage loan rates trends:
- Plan to refinance into a fixed-rate mortgage before your first adjustment, assuming rates are favorable and your credit is strong.
- If you’re in a high-appreciation area, consider selling before the rate resets and using equity to upgrade or downsize.
- Some lenders offer ARM-to-fixed conversion options—ask about these when shopping for your loan.
Consulting Financial Advisors and Mortgage Experts
Professional guidance can make a significant difference in navigating adjustable mortgage loan rates trends:
- A certified financial planner can help assess whether an ARM aligns with your overall financial strategy.
- Mortgage brokers often have access to multiple lenders and can identify the most competitive ARM products.
- HUD-approved housing counselors offer free or low-cost advice on mortgage options and risks.
What are adjustable mortgage loan rates trends?
Adjustable mortgage loan rates trends refer to the changes in interest rates for adjustable-rate mortgages over time. These trends are influenced by economic factors like inflation, Federal Reserve policy, and bond market conditions, and they affect monthly payments for ARM borrowers.
Are ARMs a good idea in 2024?
ARMs can be a smart choice in 2024 for borrowers who plan to stay in their homes for a short period or expect rates to fall. However, they carry risk if rates rise, so they’re best suited for financially flexible individuals with a clear exit strategy.
How often do ARM rates adjust?
After the initial fixed period (e.g., 5 years for a 5/1 ARM), the rate typically adjusts annually. The frequency and limits of adjustments are defined in your loan agreement, including periodic and lifetime caps.
What index do ARMs use in 2024?
Most ARMs in 2024 are tied to the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR), which replaced LIBOR as the primary benchmark. The rate is calculated as SOFR plus a lender-specific margin.
Can I refinance an ARM to a fixed-rate mortgage?
Yes, you can refinance an ARM into a fixed-rate mortgage at any time, provided you qualify based on credit, income, and home equity. Refinancing before the first rate adjustment is a common strategy to lock in stability.
Understanding adjustable mortgage loan rates trends is more important than ever in today’s dynamic financial landscape. While ARMs offer attractive short-term savings, they come with long-term uncertainties that demand careful planning. By staying informed, monitoring economic indicators, and preparing for potential rate increases, borrowers can make smarter decisions that align with their financial goals. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or a seasoned investor, leveraging the latest data and expert insights will help you navigate the evolving world of mortgage financing with confidence.
Further Reading: